Zero-Sum Games and AI
- A player's utility gain or loss is exactly balanced by the combined gain or loss of opponents → 어느 한 플레이어에게 이득인것은 반대편 플레이어에게는 손해여야한다.
- This is a powerful concept important to AI development for measuring the cost/benefit of a particular move
- Nash Equilibrium
Games and AI
- Traditional strategy - Minimax:
- Attempt to minimize opponent's maximum reward at each state (Nash Equilibrium) → 내쉬균형에 따라 상대편의 이익은 최소화하고, 나의 이익을 최대화하려는 알고리즘
- Exhaustive Search → 많은 상태공간의 탐색이 필요하다
2024.11.04 - [[학교 수업]/[학교 수업] 인공지능] - [인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm
[인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm
Min-Max Search Min-max algoritm is applied in two player gamesexample: chess, go, tic-tac-toe, and so on. The characteristics of two-player gamesLogic game: the game can be described by a set of rules and promisesFull information games: it is possible to
hw-hk.tistory.com
Drawbacks
- The number of moves to be analyzed quickly increases in depth → 깊이가 깊어질수록, 분석해야하는 움직임의 수가 빠르게 증가한다
- The computation power limits how deep the algorithm can go → 계산적 한계가 있다
- It is difficult to solve a complex game in a finite amount of time → 복잡한 문제에 적용하기 어렵다
- Games like cheakers and chess can arguably be solved using the minimax algorithms state (branch factors ≒ 30)
- Things can ge t a little tricky when there are a large nuber of potential actions to be taken at each state (branch factors ≒ 300)
Alternative idea
- Bandit-based Methods
- Choosing between K actions/moves → minimax는 모든 가능한 움직임을 계산한 것과 달리...
- Need to maximize the cumulative reward by continuously picking the best move → 누적 reward를 최대화하는 방식을 사용하는데, 이는 휴리스틱과 같은 평가함수를 사용하지 않는다
- Bandit-based methods have been used for tree search, because of their efficient trade-off between → bandit-based method는 아래의 두 가지의 특징의 밸런스를 잘 잡았다
- Exploration of the most uncertain branches and → 탐색, 탐험, tree의 너비를 넓히는 행동
- Exploitation of the most promising ones → 개발, tree의 깊이를 깊게하는 행동
- Finally leading to very promising results in dealing with huge trees
- Upper confidence bound (UDB) bandit algorithms applied to tree search: UCT (upper confidence bounds applied to Trees) → 이런 UCB를 tree에 적용한 것을 UCT라고 한다
Monte Carlo Tree Search
- Application of the Bandit-based methods
- Two fundamental concepts:
- the true value of any action can be approximated by running several random simulations → MCT에서의 reward는 Minimax의 휴리스틱과 같이 어떤 함수로 평가되는 것이 아니다
- these values can be efficiently used to adjust the policy (strategy) towards a best-first strategy
- Builds a partial game tree before each move. then selection is made → 처음에는 부분게임 tree를 가지고 시작한다. 그냥 root부터 게임을 진행하면 부분트리를 만드는데, 쓸데없는 시간을 너무 많이 쓰게된다
- Moves are explored and values are updated/estimated
General Applications of Monte Carlo Methods
- Numerical Algorithms
- AI games
- Particularly games with imperfect information
- very successful in GO
- Many other applications
- Real world planning
- Optimization
- Control systems
MCTS Overview
- Iteratively building partial search tree
- Iteration
- Most urgent node
- tree policy
- Exploration/Exploitation
- Simulation
- Add child node
- Default policy
- Update weight
- Most urgent node
Algorithms Overview
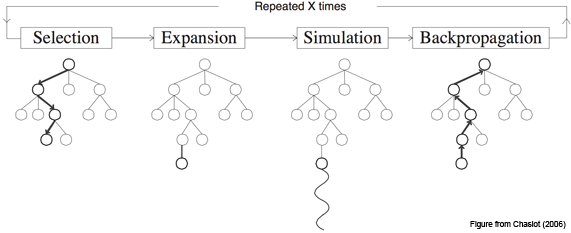
- Selection
- Selecting good child nodes, starting the root node
- 루트 노드에서 시작해 좋은 노드를 선택하는 작업, UCT에 의해 선택된다
- Expansion
- If L is a not terminal node, then create one or more child nodes and select one (C)
- Tree를 확장하는 작업
- Simulation (rollout)
- Run a simulated playout from C until a result is achieved
- 선택한 terminal node에 대해 시뮬레이션을 시작한 후, 누적 reward를 측정
- Backpropagation
- Update the current move sequence with the simulation result
- 시뮬레이션의 결과를 다른 노드들에 적용하는 작업
Policies
- Policies are crucial for how MCTS operates
- Tree policy
- Used to determine how children are selected → Child를 선택하는 정책
- Default policy
- Used to determine how simulations are run (ex. Randomized) → 시뮬레이션 정책
- Result of simulation used to update values → 역전파 정책
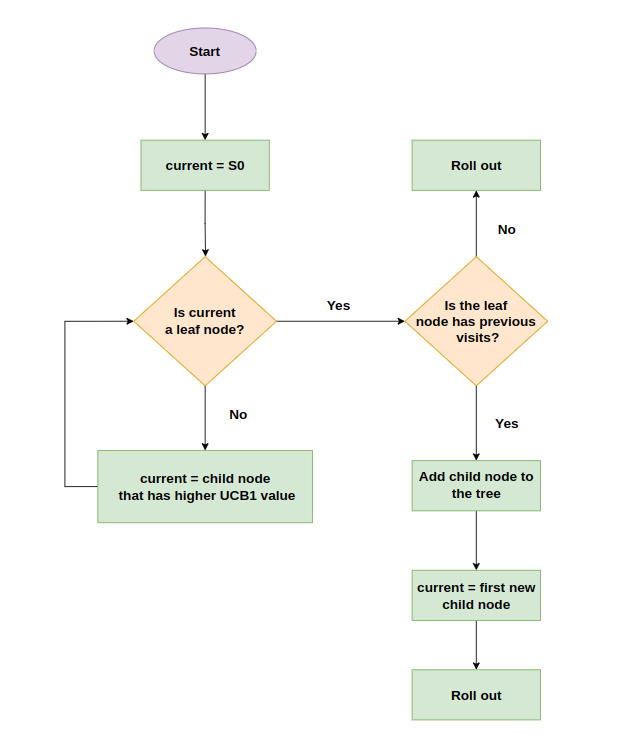
Selection
- Start at root node
- Based on tree policy select child
- Apply recursively - descend through tree
- Stop when expandable node is reached
- Expandable: node that is not-terminal and has unexplored children → 아직 탐색되지 않은 노드를 자식으로 갖는 노드가 나올때까지...
Expansion
- Add one or more child nodes to tree
- Depends on what actions are available for the current position
- Method in which this is done depends on Tree Policy → Tree policy에 따라 동작한다
Simulation
- Run simulation of path that was selected → 선택된 경로로 시뮬레이션을 시작
- Get position a end of simulation
- Default Policy determines how simulation is running → Default 정책에 의해 시뮬레이션이 어떻게 동작할지가 결정
- Board outcome determines value → reward를 얻는 노드까지 도달하는 동안의 nodes들에 대한 value를 저장하지 않기 때문에 memory의 효율성이 좋다
Backpropagation
- Moves backward through saved path
- Value of node
- Representative of benefit of going down that path
- Values are updated dependent on board outcomes
- Based on how the simulated game ends
Policies
- Tree policy
- Select/create leaf node
- Selection and expansion
- Bandit problem! → Exploration과 Exploitation의 조화를 맞추는 문제
- Default policy
- Play the game till end
- Simulation
- Selection the best child
- Max (highest weight) → Simulation value를 신뢰하는 경우 → 게임의 후반 (simulation의 길이가 짧아서 value의 신뢰도가 높다)
- Robust (most visits) → Simulation value를 신뢰하지 않는 경우 → 게임의 초반 (Tree policy를 신뢰)
- Max-robust (both, iterate if none exists) → 같이...
UCT Algorithm
- Selecting child node: Multi-Arm Bandit Problem
- UCB1 for each child selection
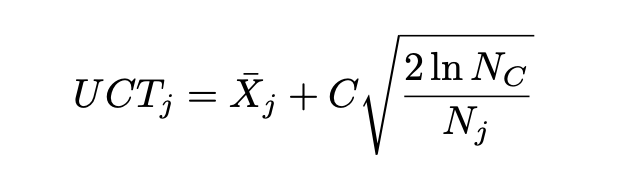
- Nc: number of times current (parent) node has been visited
- Nj: number of times child j has been visited
- C: some constant > 0
- Xj: mean reward of selectiong this position [0,1]
+ 한 번도 search가 되지 않은 child node의 경우 Nj가 0이므로 UCT값이 무한대가 되어서 반드시 탐색하게 된다
+ 왼쪽의 항, 즉 평균 reward는 Exploitation을 의미, 오른쪽의 항은 Exploration을 의미한다. 즉, 상수값 C를 통해 이 둘의 밸런스를 맞출 수 있다
Advantages/Disadvantages of MCTS
- Aheuristic
- No need for domain-specific knowledge
- Other algorithms may work better if heuristic exists
- Minimax for chess
- Better because chess has strong heuristics that can decrease size of tree
- 배경지식이 없어도 된다는 장점이 있다
- Anytime
- Can stop running MCTS at any time
- Return best action
- Asymmetric
- Favor more promising nodes with UCT
- 비대칭성으로인해 원하는 노드만 탐색할 수 있다
'[학교 수업] > [학교 수업] AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [인공지능] 지식 표현과 추론 (1) | 2024.11.29 |
|---|---|
| [인공지능] Genetic Algorithm (1) | 2024.11.25 |
| [인공지능] Quarto Team Project - MCTS Parallelization (2) | 2024.11.10 |
| [인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm (1) | 2024.11.04 |
| [인공지능] 경험적 탐색 (1) | 2024.11.01 |
Zero-Sum Games and AI
- A player's utility gain or loss is exactly balanced by the combined gain or loss of opponents → 어느 한 플레이어에게 이득인것은 반대편 플레이어에게는 손해여야한다.
- This is a powerful concept important to AI development for measuring the cost/benefit of a particular move
- Nash Equilibrium
Games and AI
- Traditional strategy - Minimax:
- Attempt to minimize opponent's maximum reward at each state (Nash Equilibrium) → 내쉬균형에 따라 상대편의 이익은 최소화하고, 나의 이익을 최대화하려는 알고리즘
- Exhaustive Search → 많은 상태공간의 탐색이 필요하다
2024.11.04 - [[학교 수업]/[학교 수업] 인공지능] - [인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm
[인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm
Min-Max Search Min-max algoritm is applied in two player gamesexample: chess, go, tic-tac-toe, and so on. The characteristics of two-player gamesLogic game: the game can be described by a set of rules and promisesFull information games: it is possible to
hw-hk.tistory.com
Drawbacks
- The number of moves to be analyzed quickly increases in depth → 깊이가 깊어질수록, 분석해야하는 움직임의 수가 빠르게 증가한다
- The computation power limits how deep the algorithm can go → 계산적 한계가 있다
- It is difficult to solve a complex game in a finite amount of time → 복잡한 문제에 적용하기 어렵다
- Games like cheakers and chess can arguably be solved using the minimax algorithms state (branch factors ≒ 30)
- Things can ge t a little tricky when there are a large nuber of potential actions to be taken at each state (branch factors ≒ 300)
Alternative idea
- Bandit-based Methods
- Choosing between K actions/moves → minimax는 모든 가능한 움직임을 계산한 것과 달리...
- Need to maximize the cumulative reward by continuously picking the best move → 누적 reward를 최대화하는 방식을 사용하는데, 이는 휴리스틱과 같은 평가함수를 사용하지 않는다
- Bandit-based methods have been used for tree search, because of their efficient trade-off between → bandit-based method는 아래의 두 가지의 특징의 밸런스를 잘 잡았다
- Exploration of the most uncertain branches and → 탐색, 탐험, tree의 너비를 넓히는 행동
- Exploitation of the most promising ones → 개발, tree의 깊이를 깊게하는 행동
- Finally leading to very promising results in dealing with huge trees
- Upper confidence bound (UDB) bandit algorithms applied to tree search: UCT (upper confidence bounds applied to Trees) → 이런 UCB를 tree에 적용한 것을 UCT라고 한다
Monte Carlo Tree Search
- Application of the Bandit-based methods
- Two fundamental concepts:
- the true value of any action can be approximated by running several random simulations → MCT에서의 reward는 Minimax의 휴리스틱과 같이 어떤 함수로 평가되는 것이 아니다
- these values can be efficiently used to adjust the policy (strategy) towards a best-first strategy
- Builds a partial game tree before each move. then selection is made → 처음에는 부분게임 tree를 가지고 시작한다. 그냥 root부터 게임을 진행하면 부분트리를 만드는데, 쓸데없는 시간을 너무 많이 쓰게된다
- Moves are explored and values are updated/estimated
General Applications of Monte Carlo Methods
- Numerical Algorithms
- AI games
- Particularly games with imperfect information
- very successful in GO
- Many other applications
- Real world planning
- Optimization
- Control systems
MCTS Overview
- Iteratively building partial search tree
- Iteration
- Most urgent node
- tree policy
- Exploration/Exploitation
- Simulation
- Add child node
- Default policy
- Update weight
- Most urgent node
Algorithms Overview
- Selection
- Selecting good child nodes, starting the root node
- 루트 노드에서 시작해 좋은 노드를 선택하는 작업, UCT에 의해 선택된다
- Expansion
- If L is a not terminal node, then create one or more child nodes and select one (C)
- Tree를 확장하는 작업
- Simulation (rollout)
- Run a simulated playout from C until a result is achieved
- 선택한 terminal node에 대해 시뮬레이션을 시작한 후, 누적 reward를 측정
- Backpropagation
- Update the current move sequence with the simulation result
- 시뮬레이션의 결과를 다른 노드들에 적용하는 작업

Policies
- Policies are crucial for how MCTS operates
- Tree policy
- Used to determine how children are selected → Child를 선택하는 정책
- Default policy
- Used to determine how simulations are run (ex. Randomized) → 시뮬레이션 정책
- Result of simulation used to update values → 역전파 정책
Selection
- Start at root node
- Based on tree policy select child
- Apply recursively - descend through tree
- Stop when expandable node is reached
- Expandable: node that is not-terminal and has unexplored children → 아직 탐색되지 않은 노드를 자식으로 갖는 노드가 나올때까지...
Expansion
- Add one or more child nodes to tree
- Depends on what actions are available for the current position
- Method in which this is done depends on Tree Policy → Tree policy에 따라 동작한다
Simulation
- Run simulation of path that was selected → 선택된 경로로 시뮬레이션을 시작
- Get position a end of simulation
- Default Policy determines how simulation is running → Default 정책에 의해 시뮬레이션이 어떻게 동작할지가 결정
- Board outcome determines value → reward를 얻는 노드까지 도달하는 동안의 nodes들에 대한 value를 저장하지 않기 때문에 memory의 효율성이 좋다

Backpropagation
- Moves backward through saved path
- Value of node
- Representative of benefit of going down that path
- Values are updated dependent on board outcomes
- Based on how the simulated game ends
Policies
- Tree policy
- Select/create leaf node
- Selection and expansion
- Bandit problem! → Exploration과 Exploitation의 조화를 맞추는 문제
- Default policy
- Play the game till end
- Simulation
- Selection the best child
- Max (highest weight) → Simulation value를 신뢰하는 경우 → 게임의 후반 (simulation의 길이가 짧아서 value의 신뢰도가 높다)
- Robust (most visits) → Simulation value를 신뢰하지 않는 경우 → 게임의 초반 (Tree policy를 신뢰)
- Max-robust (both, iterate if none exists) → 같이...
UCT Algorithm
- Selecting child node: Multi-Arm Bandit Problem
- UCB1 for each child selection
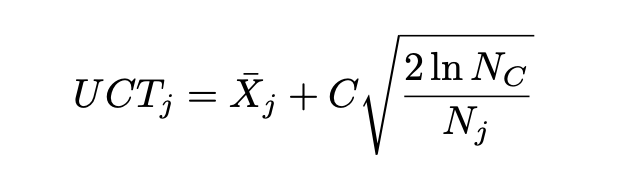
- Nc: number of times current (parent) node has been visited
- Nj: number of times child j has been visited
- C: some constant > 0
- Xj: mean reward of selectiong this position [0,1]
+ 한 번도 search가 되지 않은 child node의 경우 Nj가 0이므로 UCT값이 무한대가 되어서 반드시 탐색하게 된다
+ 왼쪽의 항, 즉 평균 reward는 Exploitation을 의미, 오른쪽의 항은 Exploration을 의미한다. 즉, 상수값 C를 통해 이 둘의 밸런스를 맞출 수 있다
Advantages/Disadvantages of MCTS
- Aheuristic
- No need for domain-specific knowledge
- Other algorithms may work better if heuristic exists
- Minimax for chess
- Better because chess has strong heuristics that can decrease size of tree
- 배경지식이 없어도 된다는 장점이 있다
- Anytime
- Can stop running MCTS at any time
- Return best action
- Asymmetric
- Favor more promising nodes with UCT
- 비대칭성으로인해 원하는 노드만 탐색할 수 있다

'[학교 수업] > [학교 수업] AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [인공지능] 지식 표현과 추론 (1) | 2024.11.29 |
|---|---|
| [인공지능] Genetic Algorithm (1) | 2024.11.25 |
| [인공지능] Quarto Team Project - MCTS Parallelization (2) | 2024.11.10 |
| [인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm (1) | 2024.11.04 |
| [인공지능] 경험적 탐색 (1) | 2024.11.01 |
