Combinatorial Optimization (CO)
- Many computer science problems deal with the choice of a best set of parameters to achieve some goal
- Example
- Placement and routing problem in VLSI design
- The traveling salesman problem
- 굉장히 복잡한 해공간을 갖는 문제
Approaches to CO
- Heuristic search (Informed Search)
- Using a function that evaluates the quality of assignment, for example, the number of constraints violated by the assignment
- Hill climbing, best-first search, A*, beam search
- Local search (i.e., Hill climbing, beam search)
- Partial search algorithm
- Modifying the value that is close to the previous one in the search space of assignment
- Iteratively improving an assignment of the variables until all constraints are satisfied
- An imcomplete method for finding a solution to a problem in constraint satisfaction
- 부분 탐색 알고리즘으로 이전 상태와 비슷한 다음 상태로 나아가는 방법
- 이를 반복하며 문제를 해결하는 것으로 완전하지는 않은 방법이지만, 효율적
Local search
- Basic Idea: Improve the current solution
- Start with some solution → initial state
- Find a set of solutions (called neighbors) that are "close" to the current solution - Neighborhood search
- If one of these neighbor are better than the current solution, move to that solution
- Repeat until no improvements can be made → It might be local optima
- Variations
- First Improvement (select the first improving neighbor) → concern with speed
- Best Improvement (always select the best neighbor) → concern with correctness
- Random Walk (move to neighbrs at random) → MCTS의 simulation phase, 그나마 local optima에 빠지는 것을 막을 수 있다
- Problem: Get stuck in a local optima
- Except random walk, which isn't a good method anyway → time이 늘어나기 때문에, 따라서 요즘은 완전 random보다는 확률에 기반한 randomness를 선호
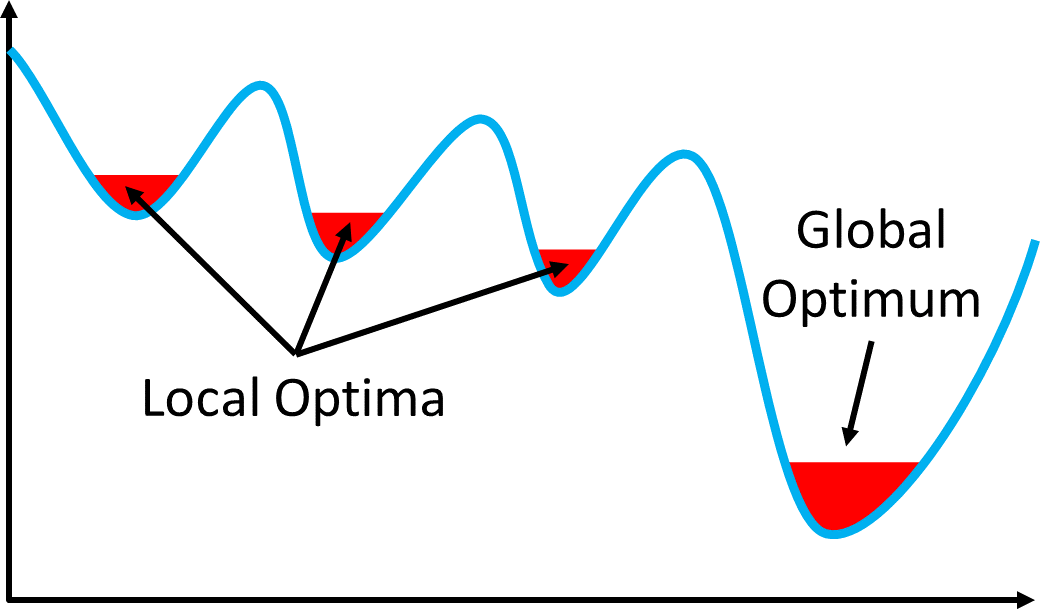
Metaheuristics
- Main goal
- To avoid getting stuck in local optima
- global optima를 지향하되, near global optima를 목표로 하는...
- Additional goals
- Explore a larger part of the search space → Neighbor size, beam search
- Attempt to find the global (not just a local) optima
- Give a reasonable alternative to exact methods (especially for large/hard problem instances, and where the solution time is important) → 합리적인 대안을 찾아줄 수 있다. CO는 해공간이 너무 복잡하기 때문에 global optima를 찾는 것이 거의 불가능하다
- The different methods employ very different techniques to escape local optima
- Local search metaheuristics
- Simulated Annealing (SA) → 탐색을 계속하면 온도가 높아지고, 온도가 너무 높아지면 그때 randomness를 적용, 이는 해공간이 커도 유용하다
- Iterated local search (ILS), multi-start local search (MLS) → 해공간이 작아야 유용
- Tabu search (TS) → memory를 이용해서 shoulder or flat문제를 해결
- Population based metaheuristics
- Genetic Algorithms (GA) → GA는 병렬화가 가능하기 때문에 탐색 시간이 적다
- ...
Genetic Algorithm
- We have now studied many metaheuristics based on Local Search
- It is time to look at methods that are based on different mechanisms
- GA
- Population based Metaheurisitc → Local search → partial search → GA도 local optima를 찾는것이다
- Based on genetics:
- Mutation → exploration
- Combination of chromosomes from parents → exploitation
- Basic idea
- Intelligent exploration of the search space based on random search → 랜덤성을 통해 지능적인 exploration을 수행한다. 랜덤성을 사용하기 때문에 세대를 거듭할수록 무조건 좋아지지는 않을 수 있다
- Analogies from biology
GA - Analogies with biology
- Representation of complex objects by a vector of simple components
- Chromosomes → Individual with binary encoding
- Selective breeding
- Darwinistic evolution → create next generation or population
- Classic GA: Binary encoding
GA - Terminology

Chromosome
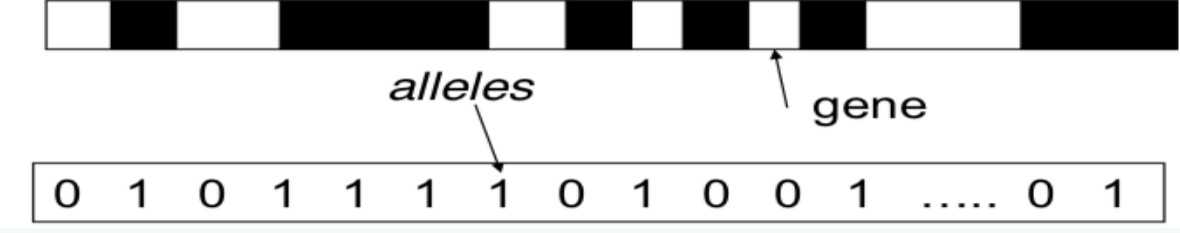
- Each chromosome represents a solution, often using strings of 0's and 1's
- Each bit typically corresponds to a gene → This is called binary encoding
- The values for a given gene are the alleles
Basic Components: Creating a GA on computer
- Define the representation (encoding - decoding techniques)
- Define "fitness" function → 어려움. meta-heuristic이긴 하지만 이 단계에서는 domain knowledge가 필요
- Define the genetic operation (i.e., Initialization, selection, crossover, mutation, insertion)
- Execute initial algorithm run → Monitoring average population fitness to check convergence
- Tune algorithm (parameter setting) → Adjust selection, insertion stretagy, mutation rate
Basic Components: 1) encoding - decoding
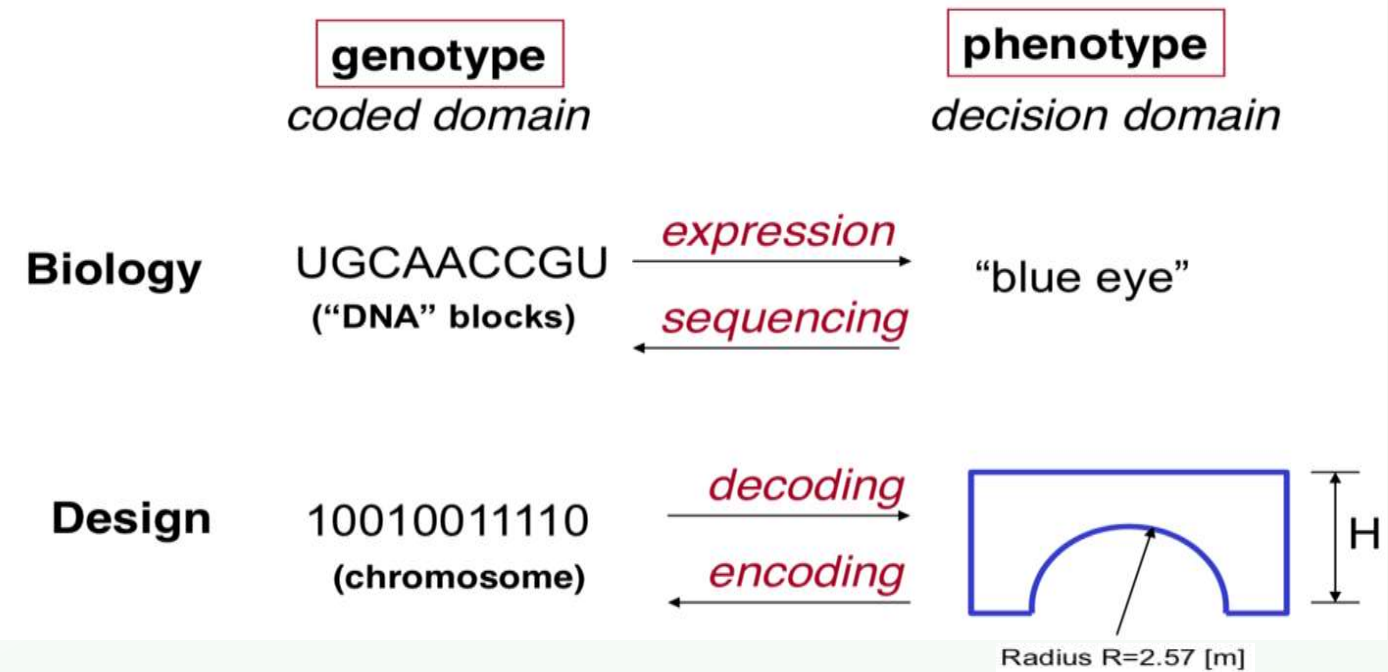
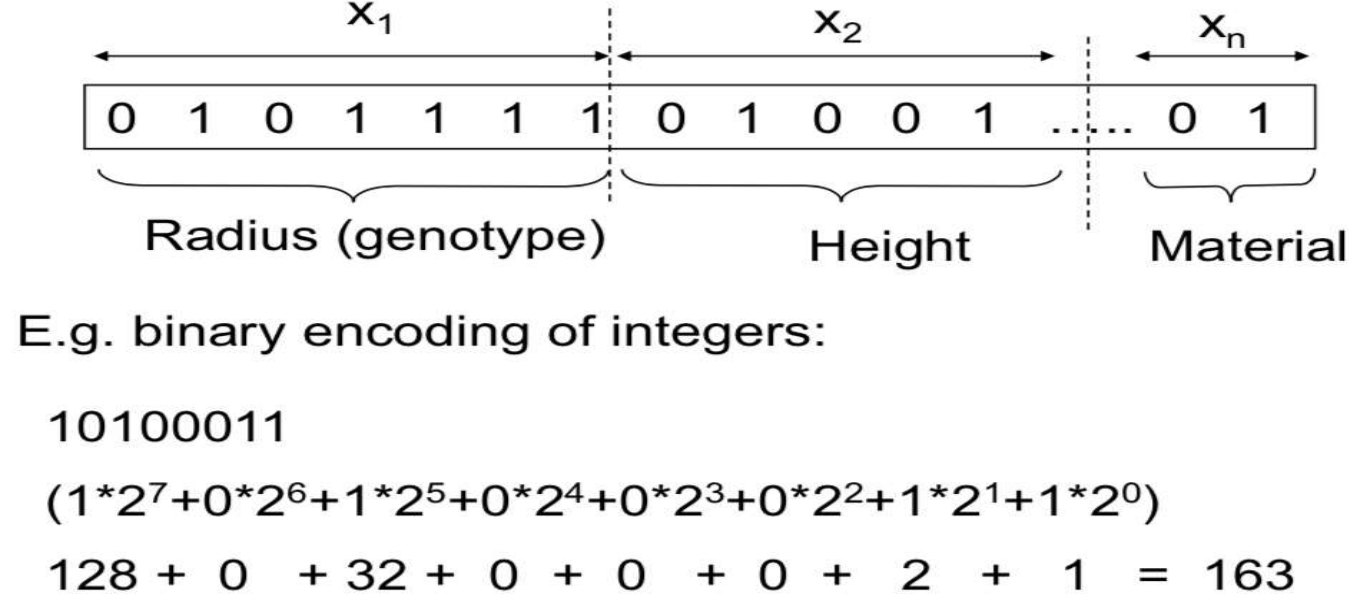
+ encoding - decoding이 쉬워야 overheads가 적다
Other Encoding Schemes
- Not all GA chromosome are binary string
- Can use different ALPHABET for GA coding
- Most common is binary alphabet {0,1}
- Can also have
- integer, real valued, Hexadecimal ...
Basic Components: 2) Fitness and Selection Probability
- Typically, selection is the most important and most computationally expensive step of a GA
- Fitness함수를 통해 수렴성을 알 수 있고, 또한 selection에 영향을 준다
- Fitness function = object function + constraints
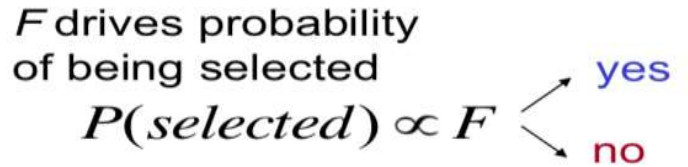
+ Fitness 값이 높을 수록, 선택될 확률이 올라간다. 이는 우성을 의미한다. 하지만 열성이 아에 선택이 되지 않는 것은 아니다. 즉 확률에 기반한 랜덤성이다.
- Fitness function
- represents how good a solution to the problem it is
- can be the objective function in the optimization problem, or subjective evaluation function
- should be normalized to the positive values → fitness값은 반드시 정규화를 거쳐야한다
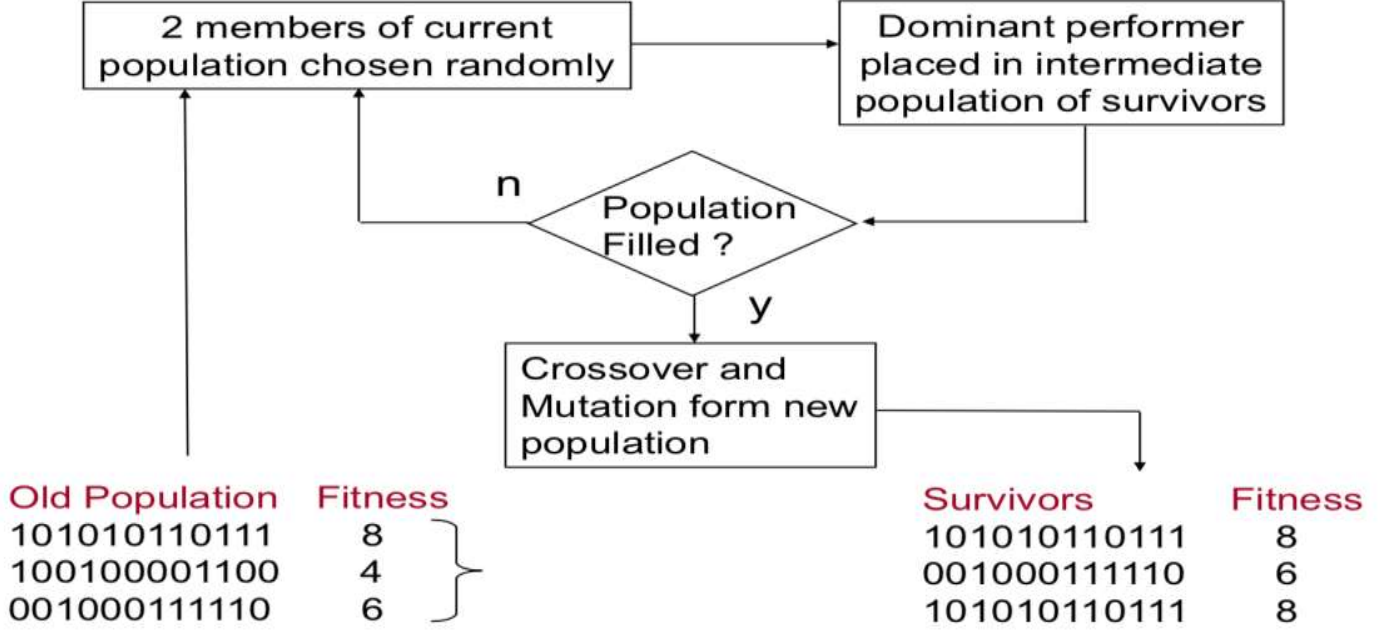
Basic Components: 3) Selection
- A process to copy parent chromosomes (crossover and mutation) into new population for genetic operations
- Ranking selection
- Sort all hypotheses by fitness
- Probability of selection is proportional to rank
- Example: select the kth most fit member of population → randomness가 굉장히 적고, exploitation이 굉장히 큰 방법이다. 이는 해공간이 작은 경우 빠르게 찾을 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 계속 좋은 것만 탐색 Only up-hill search
- Proportionate selection (roulette-wheel selection)
- Pick h in proportion to its fitness → 모든 가능한 노드들에 대해 fitness값을 구해야하기 때문에 연산시간이 길다. Ranking과 달리 확률기반 randomness이다
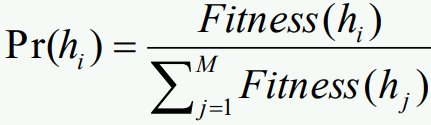
- Tournament selection
- Pick h1, h2 at random with uniform probability
- With probability p, select the more fit → 좋은 노드를 선택 (Ranking) but 모두 정렬하지는 않는다 (랜덤성). 확률을 기반으로 (Roulette) but 모든 노드들의 확률을 계산하지는 않는다 (연산시간 단축).

+ 토너먼트 방식의 경우 중복된 염색체가 선택될 수도 있다. 하지만 이는 crossover단계에서 걸러지기도 한다.
Basic Components: 4) Crossover
- An operation to exchange information between randomly selected parent chromosomes
- Its purpose is not losing any important information of parent chromosomes
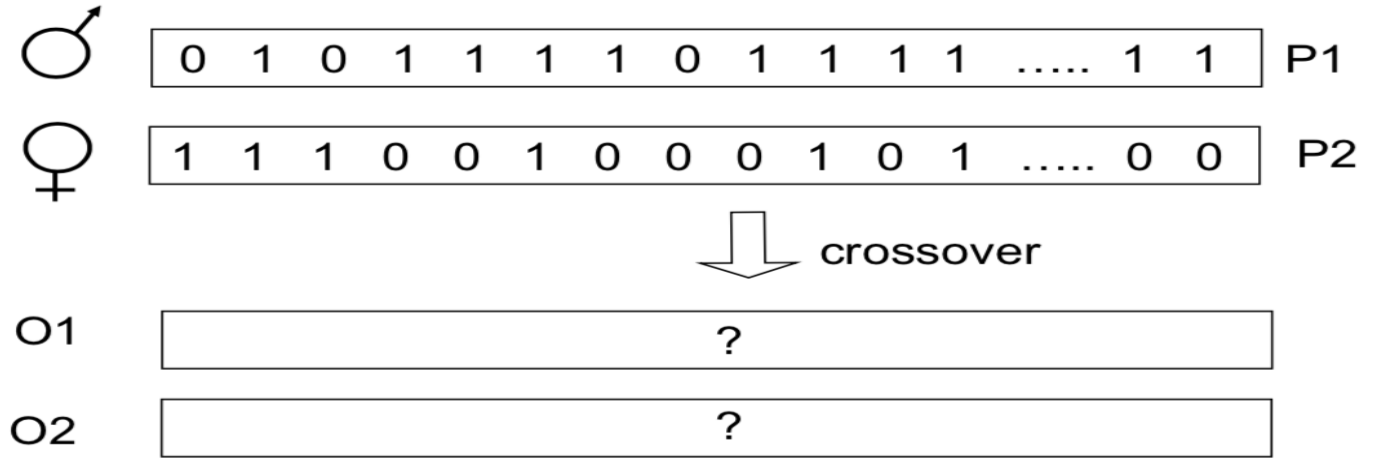
- Crossover is taking 2 solutions, and creating 1 or 2 more
- Sigle-point crossover
- Multi-point crossover
- Uniform crossover → 하나의 binary마다 동일한 확률로 선택

Example: one-point crossover
- Classical: single point crossover
- A crossover bit '|' is chosen (deliberately or randomly), splitting the chromosome in half
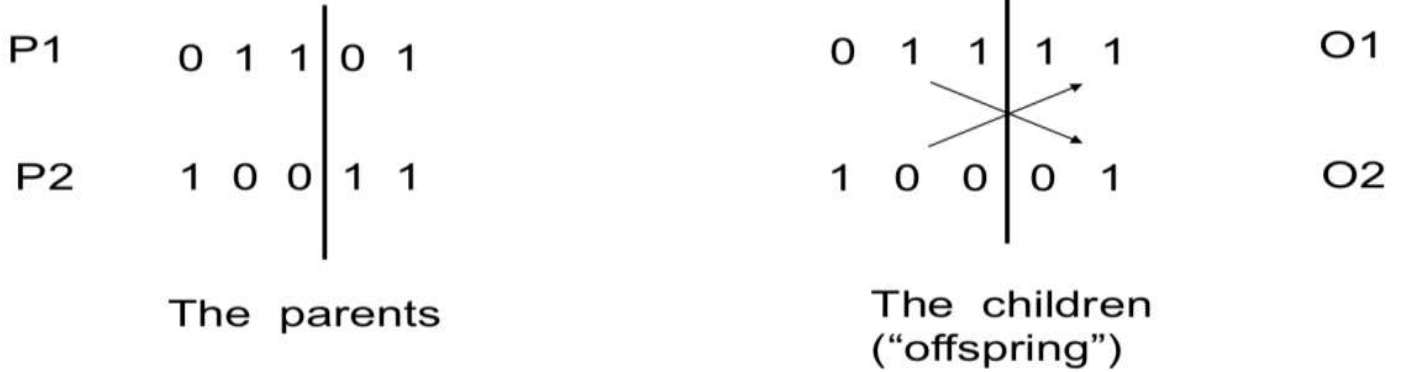
Example: uniform crossover → Randomness↑, time↓
- Assign 'heads' to one parent, 'tails' to the other
- Flip a coin for each gene of the first child
- Make an inverse copy of the gene for the second child
- Inheritance is independent of position
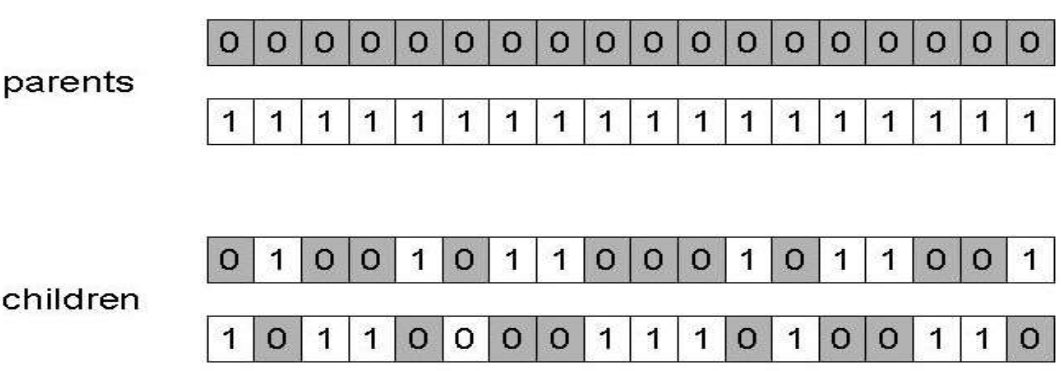
Basic Components: 5) Mutation
- An operator to randomly alter each gene
- Its aim is to introduce genetic diversity into the population

Basic Components: 6) Some Insertion Strategies
- Can replace an entire population at a time (go from generation k to k+1 with no survivors)
- Select N/2 pairs of parents (N is # of members in population)
- Create N children, replace all parents
- Polygamy is generally allowed
- Can select two parents at a time
- Create a child
- Eliminate one member of population (weakest?)
- Elitist strategy
- small number of fittest individuals survivie unchanged → Randomness ↓
- 적은 수의 가장 잘 맞는 염색체는 바꾸지 않고 살려둔다
- Hall-of-frame
- Remember best past individuals, but don't use them for progeny
- 최상의 염색체는 기억하되, 자손에 사용하지는 않는다
Basic Components: 7) Initialization
- Somehow we need to create an initial population of solutions to start the GA
- Typical goal: Select an initial population that has both quality and diversity
- How can this be done?
- Random initial population, one of many options
- Use random number generator to create initial population (caution with seeds!)
- Typically use uniform probability density functions (pdf's)
GA Convergence
- Average perfomance of individuals in a population is expected to increase, as good individuals are preserved and bred and less fit individual die out
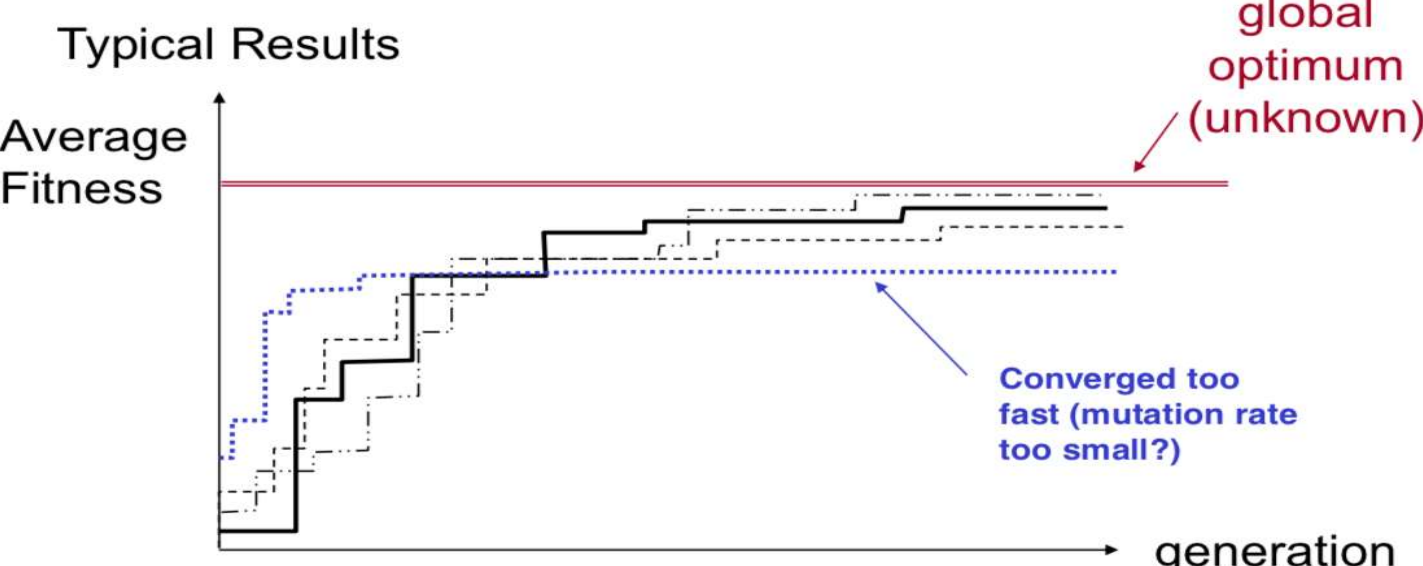
+ 수렴의 속도가 너무 빠르다면 local optima에 빠졌음을 예측할 수 있다. 그렇다면 randomness를 늘리는 해결방법을 생각할 수 있다.
Basic Components: 8) GA control parameters
- Population size (M) → 개체수가 커진다면, 병렬성이 증가하는 것으로 수렴속도가 빨라질 수 있다. 하지만 memory cost가 커질 수 있다
- Mutation rate (Pm) (0.01 ~ 0.05) → Pm이 커진다면 randomness가 커진다
- Crossover rate (Pc) (0.1 ~ 0.5) → 선택된 부모들 사이에서 crossover가 일어날 확률, selection이 일어나는 부모의 수를 의미한다
Example1: function optimization
Example2: TSP
+ TSP의 경우는 유전자의 crossover나 mutation단계에서 제약조건들이 많다 (예를 들어, 여행가는 도시의 순서가 의미가 있고, 도시가 중복될 수 없기 때문에 아무렇게나 crossover나 mutation을 할 수 없다).
+ 따라서 crossover는 order-based crossover를 사용한다.
+ Mutation또한 reodering of the list를 사용한다.
Appendix
A Complete Guide to Genetic Algorithm — Advantages, Limitations & More
Optimization algorithms execute iterative operations to come up with numerous solutions and then compare those to reach the optimum…
medium.com
'[학교 수업] > [학교 수업] AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [인공지능] Fuzzy Inference (2) | 2024.11.29 |
|---|---|
| [인공지능] 지식 표현과 추론 (1) | 2024.11.29 |
| [인공지능] Game Tree Search (2) - Monte Carlo Tree Search (0) | 2024.11.25 |
| [인공지능] Quarto Team Project - MCTS Parallelization (2) | 2024.11.10 |
| [인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm (1) | 2024.11.04 |
Combinatorial Optimization (CO)
- Many computer science problems deal with the choice of a best set of parameters to achieve some goal
- Example
- Placement and routing problem in VLSI design
- The traveling salesman problem
- 굉장히 복잡한 해공간을 갖는 문제
Approaches to CO
- Heuristic search (Informed Search)
- Using a function that evaluates the quality of assignment, for example, the number of constraints violated by the assignment
- Hill climbing, best-first search, A*, beam search
- Local search (i.e., Hill climbing, beam search)
- Partial search algorithm
- Modifying the value that is close to the previous one in the search space of assignment
- Iteratively improving an assignment of the variables until all constraints are satisfied
- An imcomplete method for finding a solution to a problem in constraint satisfaction
- 부분 탐색 알고리즘으로 이전 상태와 비슷한 다음 상태로 나아가는 방법
- 이를 반복하며 문제를 해결하는 것으로 완전하지는 않은 방법이지만, 효율적
Local search
- Basic Idea: Improve the current solution
- Start with some solution → initial state
- Find a set of solutions (called neighbors) that are "close" to the current solution - Neighborhood search
- If one of these neighbor are better than the current solution, move to that solution
- Repeat until no improvements can be made → It might be local optima
- Variations
- First Improvement (select the first improving neighbor) → concern with speed
- Best Improvement (always select the best neighbor) → concern with correctness
- Random Walk (move to neighbrs at random) → MCTS의 simulation phase, 그나마 local optima에 빠지는 것을 막을 수 있다
- Problem: Get stuck in a local optima
- Except random walk, which isn't a good method anyway → time이 늘어나기 때문에, 따라서 요즘은 완전 random보다는 확률에 기반한 randomness를 선호

Metaheuristics
- Main goal
- To avoid getting stuck in local optima
- global optima를 지향하되, near global optima를 목표로 하는...
- Additional goals
- Explore a larger part of the search space → Neighbor size, beam search
- Attempt to find the global (not just a local) optima
- Give a reasonable alternative to exact methods (especially for large/hard problem instances, and where the solution time is important) → 합리적인 대안을 찾아줄 수 있다. CO는 해공간이 너무 복잡하기 때문에 global optima를 찾는 것이 거의 불가능하다
- The different methods employ very different techniques to escape local optima
- Local search metaheuristics
- Simulated Annealing (SA) → 탐색을 계속하면 온도가 높아지고, 온도가 너무 높아지면 그때 randomness를 적용, 이는 해공간이 커도 유용하다
- Iterated local search (ILS), multi-start local search (MLS) → 해공간이 작아야 유용
- Tabu search (TS) → memory를 이용해서 shoulder or flat문제를 해결
- Population based metaheuristics
- Genetic Algorithms (GA) → GA는 병렬화가 가능하기 때문에 탐색 시간이 적다
- ...
Genetic Algorithm
- We have now studied many metaheuristics based on Local Search
- It is time to look at methods that are based on different mechanisms
- GA
- Population based Metaheurisitc → Local search → partial search → GA도 local optima를 찾는것이다
- Based on genetics:
- Mutation → exploration
- Combination of chromosomes from parents → exploitation
- Basic idea
- Intelligent exploration of the search space based on random search → 랜덤성을 통해 지능적인 exploration을 수행한다. 랜덤성을 사용하기 때문에 세대를 거듭할수록 무조건 좋아지지는 않을 수 있다
- Analogies from biology
GA - Analogies with biology
- Representation of complex objects by a vector of simple components
- Chromosomes → Individual with binary encoding
- Selective breeding
- Darwinistic evolution → create next generation or population
- Classic GA: Binary encoding
GA - Terminology

Chromosome

- Each chromosome represents a solution, often using strings of 0's and 1's
- Each bit typically corresponds to a gene → This is called binary encoding
- The values for a given gene are the alleles
Basic Components: Creating a GA on computer
- Define the representation (encoding - decoding techniques)
- Define "fitness" function → 어려움. meta-heuristic이긴 하지만 이 단계에서는 domain knowledge가 필요
- Define the genetic operation (i.e., Initialization, selection, crossover, mutation, insertion)
- Execute initial algorithm run → Monitoring average population fitness to check convergence
- Tune algorithm (parameter setting) → Adjust selection, insertion stretagy, mutation rate
Basic Components: 1) encoding - decoding


+ encoding - decoding이 쉬워야 overheads가 적다
Other Encoding Schemes
- Not all GA chromosome are binary string
- Can use different ALPHABET for GA coding
- Most common is binary alphabet {0,1}
- Can also have
- integer, real valued, Hexadecimal ...
Basic Components: 2) Fitness and Selection Probability
- Typically, selection is the most important and most computationally expensive step of a GA
- Fitness함수를 통해 수렴성을 알 수 있고, 또한 selection에 영향을 준다
- Fitness function = object function + constraints
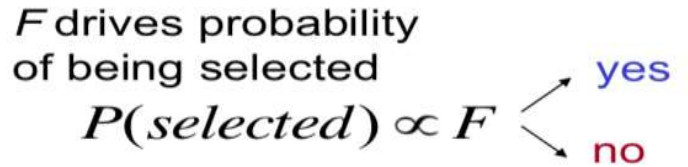
+ Fitness 값이 높을 수록, 선택될 확률이 올라간다. 이는 우성을 의미한다. 하지만 열성이 아에 선택이 되지 않는 것은 아니다. 즉 확률에 기반한 랜덤성이다.
- Fitness function
- represents how good a solution to the problem it is
- can be the objective function in the optimization problem, or subjective evaluation function
- should be normalized to the positive values → fitness값은 반드시 정규화를 거쳐야한다
Basic Components: 3) Selection
- A process to copy parent chromosomes (crossover and mutation) into new population for genetic operations
- Ranking selection
- Sort all hypotheses by fitness
- Probability of selection is proportional to rank
- Example: select the kth most fit member of population → randomness가 굉장히 적고, exploitation이 굉장히 큰 방법이다. 이는 해공간이 작은 경우 빠르게 찾을 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 계속 좋은 것만 탐색 Only up-hill search
- Proportionate selection (roulette-wheel selection)
- Pick h in proportion to its fitness → 모든 가능한 노드들에 대해 fitness값을 구해야하기 때문에 연산시간이 길다. Ranking과 달리 확률기반 randomness이다
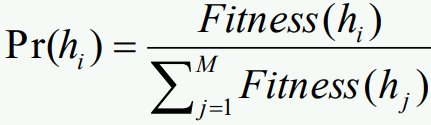
- Tournament selection
- Pick h1, h2 at random with uniform probability
- With probability p, select the more fit → 좋은 노드를 선택 (Ranking) but 모두 정렬하지는 않는다 (랜덤성). 확률을 기반으로 (Roulette) but 모든 노드들의 확률을 계산하지는 않는다 (연산시간 단축).


+ 토너먼트 방식의 경우 중복된 염색체가 선택될 수도 있다. 하지만 이는 crossover단계에서 걸러지기도 한다.
Basic Components: 4) Crossover
- An operation to exchange information between randomly selected parent chromosomes
- Its purpose is not losing any important information of parent chromosomes

- Crossover is taking 2 solutions, and creating 1 or 2 more
- Sigle-point crossover
- Multi-point crossover
- Uniform crossover → 하나의 binary마다 동일한 확률로 선택

Example: one-point crossover
- Classical: single point crossover
- A crossover bit '|' is chosen (deliberately or randomly), splitting the chromosome in half
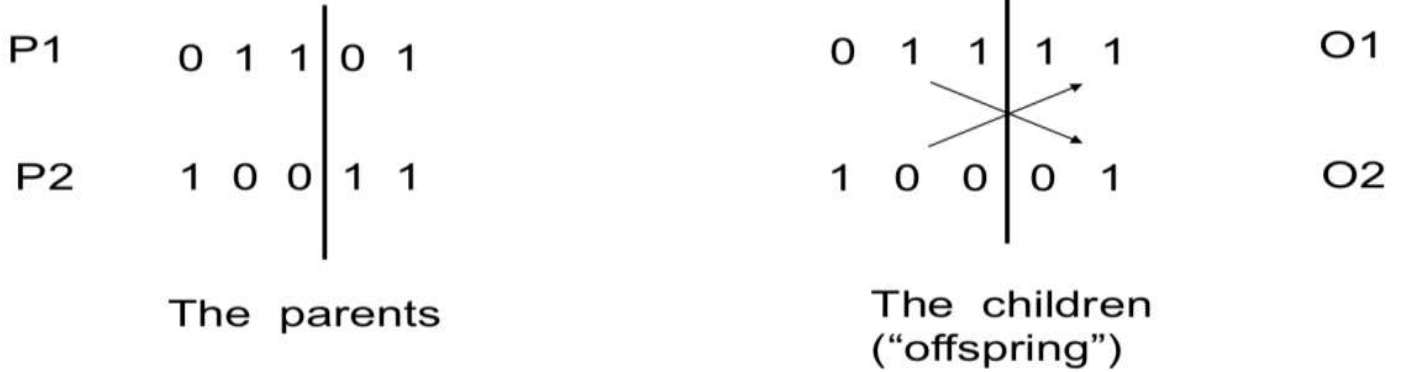
Example: uniform crossover → Randomness↑, time↓
- Assign 'heads' to one parent, 'tails' to the other
- Flip a coin for each gene of the first child
- Make an inverse copy of the gene for the second child
- Inheritance is independent of position

Basic Components: 5) Mutation
- An operator to randomly alter each gene
- Its aim is to introduce genetic diversity into the population

Basic Components: 6) Some Insertion Strategies
- Can replace an entire population at a time (go from generation k to k+1 with no survivors)
- Select N/2 pairs of parents (N is # of members in population)
- Create N children, replace all parents
- Polygamy is generally allowed
- Can select two parents at a time
- Create a child
- Eliminate one member of population (weakest?)
- Elitist strategy
- small number of fittest individuals survivie unchanged → Randomness ↓
- 적은 수의 가장 잘 맞는 염색체는 바꾸지 않고 살려둔다
- Hall-of-frame
- Remember best past individuals, but don't use them for progeny
- 최상의 염색체는 기억하되, 자손에 사용하지는 않는다
Basic Components: 7) Initialization
- Somehow we need to create an initial population of solutions to start the GA
- Typical goal: Select an initial population that has both quality and diversity
- How can this be done?
- Random initial population, one of many options
- Use random number generator to create initial population (caution with seeds!)
- Typically use uniform probability density functions (pdf's)
GA Convergence
- Average perfomance of individuals in a population is expected to increase, as good individuals are preserved and bred and less fit individual die out

+ 수렴의 속도가 너무 빠르다면 local optima에 빠졌음을 예측할 수 있다. 그렇다면 randomness를 늘리는 해결방법을 생각할 수 있다.
Basic Components: 8) GA control parameters
- Population size (M) → 개체수가 커진다면, 병렬성이 증가하는 것으로 수렴속도가 빨라질 수 있다. 하지만 memory cost가 커질 수 있다
- Mutation rate (Pm) (0.01 ~ 0.05) → Pm이 커진다면 randomness가 커진다
- Crossover rate (Pc) (0.1 ~ 0.5) → 선택된 부모들 사이에서 crossover가 일어날 확률, selection이 일어나는 부모의 수를 의미한다
Example1: function optimization
Example2: TSP
+ TSP의 경우는 유전자의 crossover나 mutation단계에서 제약조건들이 많다 (예를 들어, 여행가는 도시의 순서가 의미가 있고, 도시가 중복될 수 없기 때문에 아무렇게나 crossover나 mutation을 할 수 없다).
+ 따라서 crossover는 order-based crossover를 사용한다.
+ Mutation또한 reodering of the list를 사용한다.
Appendix
A Complete Guide to Genetic Algorithm — Advantages, Limitations & More
Optimization algorithms execute iterative operations to come up with numerous solutions and then compare those to reach the optimum…
medium.com
'[학교 수업] > [학교 수업] AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [인공지능] Fuzzy Inference (2) | 2024.11.29 |
|---|---|
| [인공지능] 지식 표현과 추론 (1) | 2024.11.29 |
| [인공지능] Game Tree Search (2) - Monte Carlo Tree Search (0) | 2024.11.25 |
| [인공지능] Quarto Team Project - MCTS Parallelization (2) | 2024.11.10 |
| [인공지능] Game Tree Search (1) - MiniMax Algoritm (1) | 2024.11.04 |
